Dec 28, 2017 Toyota Corolla repair manual, fault codes, wiring diagrams PDF free download See also: Toyota Chaser repair manual Toyota Camry repair manual Toyota Service Manuals These repair manuals covers the operation and repair of the Toyota Corolla. The book describes the repair of cars with gasoline and diesel engines 4ZZ-FE / 3ZZ-FE / 2ZZ-GE / 1CD-FTV in volume 1.4, 1.6, 1.8 and 2.0D liters with a. Toyota Car Manuals PDF & Wiring Diagrams above the page. Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki-gaisha or just short of Toyota, the largest automaker in the world.The history of this company, like most others, began with absolutely no cars, and on the looms.
- 2010 Toyota Camry Wiring Diagrams Download Pdf
- Toyota Camry 2014 Wiring Diagram
- Toyota Camry Electrical Wiring Diagram
- 2008 Toyota Camry Wiring Diagrams
- Free Toyota Wiring Diagrams
Camry Electrical Wiring Diagram
Toyota service, workshop, owner's and repair manual; electrical wiring diagrams, fault codes/ diagnostic trouble codes in PDF - free download more than 200+ Toyota manuals! 2010 Toyota Camry Hybrid Wiring Diagram Manual Original. Click on thumbnail to zoom. Condition Qty Price; Very Good. This wiring diagram shows you how to follow the wiring from bumper-to-bumper. It will help you understand connector configurations, and locate and identify circuits, relays, and grounds. 2010 Toyota Camry Hybrid Sedan 4-Door. All pages are printable, so print off what you need and take it with you into the garage or workshop. Click TOYOTA wiring diagram pdf download the same material. Furthermore, you can save it on every computer, iPad, hard disc, etc. Toyota Corolla 2009 2010 Toyota Electrical Wiring Diagrams Page Number: 482 Encrypted: no. Toyota service, workshop, owner’s and repair manual; electrical wiring diagrams, fault codes/ diagnostic trouble codes in PDF – free download more than 200+ Toyota manuals! Toyota repair manuals, owners manual & electrical wiring diagrams. Variety of 1994 toyota camry wiring diagram. A wiring diagram is a simplified conventional photographic depiction of an electric circuit. It reveals the parts of the circuit as simplified shapes, and the power and also signal links between the gadgets.
Total OBD & ECU Auto Diagnostics
Section Code
ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING G. . .
OVERALL ELECTRICAL WIRING DIAGRAM . M . . .
Page
No. | Section | |
A | INDEX | Index of the contents of this manual. |
INTRODUCTION | Brief explanation of each section. | |
B | HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL | Instructions on how to use this manual. |
C | TROUBLESHOOTING | Describes the basic inspection procedures for electrical circuits. |
D | ABBREVIATIONS | Defines the abbreviations used in this manual. |
E | GLOSSARY OF TERMS AND SYMBOLS | Defines the symbols and functions of major parts. |
F | RELAY LOCATIONS | Shows position of the Electronic Control Unit, Relays, Relay Block, etc. This section is closely related to the system circuit. |
G | ELECTRICAL WIRING ROUTING | Describes position of Parts Connectors, Splice points, Ground points, etc. This section is closely related to the system circuit. |
H | INDEX | Index of the system circuits. |
SYSTEM CIRCUITS | Electrical circuits of each system are shown from the power supply through ground points. Wiring connections and their positions are shown and classified by code according to the connection method. (Refer to the section, 'How to use this manual'). The 'System Outline' and 'Service Hints' useful for troubleshooting are also contained in this section. | |
I | GROUND POINT | Shows ground positions of all parts described in this manual. |
J | POWER SOURCE (Current Flow Chart) | Describes power distribution from the power supply to various electrical loads. |
K | CONNECTOR LIST | Describes the form of the connectors for the parts appeared in this book. This section is closely related to the system circuit. |
L | PART NUMBER OF CONNECTORS | Indicates the part number of the connectors used in this manual. |
M | OVERALL ELECTRICAL WIRING DIAGRAM | Provides circuit diagrams showing the circuit connections. |
This manual provides information on the electrical circuits installed on vehicles by dividing them into a circuit for each system.
The actual wiring of each system circuit is shown from the point where the power source is received from the battery as far as each ground point. (All circuit diagrams are shown with the switches in the OFF position.)
When troubleshooting any problem, first understand the operation of the circuit where the problem was detected (see System Circuit section), the power source supplying power to that circuit (see Power Source section), and the ground points (see Ground Point section). See the System Outline to understand the circuit operation.
When the circuit operation is understood, begin troubleshooting of the problem circuit to isolate the cause. Use Relay Location and Electrical Wiring Routing sections to find each part, junction block and wiring harness connectors, wiring harness and wiring harness connectors and ground points of each system circuit. Internal wiring for each junction block is also provided for better understanding of connection within a junction block.
Wiring related to each system is indicated in each system circuit by arrows
(from_, to_). When overall connections are required, see the Overall Electrical
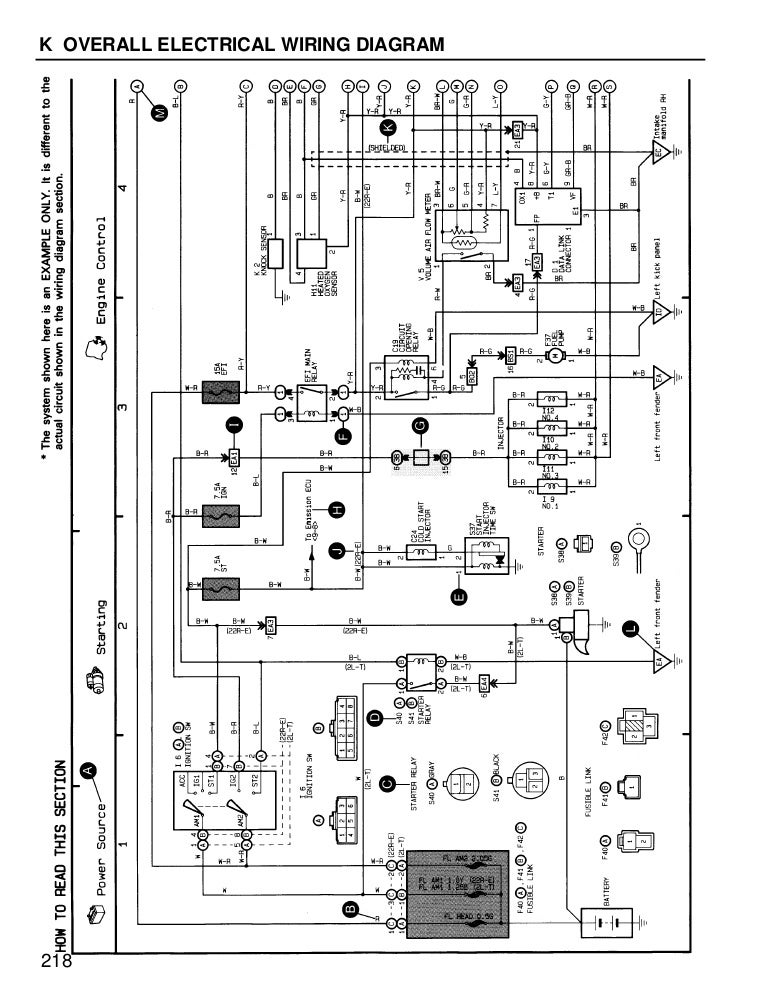
Wiring Diagram at the end of this manual.
The system shown here is an EXAMPLE ONLY. It is different to the actual circuit shown in the SYSTEM CIRCUITS SECTION.
Stop Light
- [G]
System Title
Indicates a Relay Block. No shading is used and only the Relay Block No. is shown to distinguish it from the J/B
Example: © Indicates Relay Block No.1
( ) is used to indicate different wiring and connector, etc. when the vehicle model, engine type, or specification is different.
Indicates related system.
Indicates the code for the (male and female) connectors which are used to join two wire harnesses. The connector code consists of two alphabetical and one numerical characters.
Female
2010 Toyota Camry Wiring Diagrams Download Pdf
Female
The first character of the connector code indicates the alphabetical code allocated to the wire harness which has the female connector, and the second shows that of the wire harness which has the male connector.
The third character indicates a serial number used to distinguish between the wire harness combinations in cases when more than one of the same combination of wire harnesses exist (e.g. CH1 and CH2).
Symbol ( ^ ) indicates the male terminal connector. Numbers outside connector codes indicate the pin numbers of both male and female connectors.
[F] : Represents a part (all parts are shown in sky blue).
The code is the same as the code used in parts position.
[G] : Junction Block (The number in the circle is the J/B
No. and the connector code is shown beside it). Junction Blocks are shaded to clearly separate them from other parts.
Example:
3C indicates that it is inside Junction Block No.3
Indicates the wiring color.
Wire colors are indicated by an alphabetical code.
Y = Yellow
= Orange
The first letter indicates the basic wire color and the second letter indicates the color of the stripe.
[I] : Indicates a shielded cable.
: Indicates the pin number of the connector. The numbering system is different for female and male connectors.
Toyota Camry 2014 Wiring Diagram
Example:
Numbered in other from upper left to lower right
Numbered in other from upper right to lower left n=n
Female
Male
Indicates the ground point. The code consists of the two characters: A letter and number. The first character of the code indicates the alphabetical code allocated to the wire harness. The second character indicates a serial number used to distinguish between the ground points in cases when more than one ground point exist on the same wire harness.
[M] : Indicates the ignition key position(s) when the power is supplied to the fuse(s).
[N] : Indicates a wiring Splice Point.
Example:
System Outline
Current is applied at all times through the STOP fuse to TERMINAL 2 of the stop lamp SW.
When the ignition SW is turned on, current flows from the GAUGE fuse to TERMINAL 8 of the light failure sensor, and also flows through the rear lights warning light to TERMINAL 4 of the light failure sensor.
Stop Light Disconnection Warning

When the ignition SW is turned on and the brake pedal is pressed (Stop lamp SW on), if the stop light circuit is open, the current flowing from TERMINAL 7 of the light failure sensor to TERMINALS 1, 2 changes, so the light failure sensor detects the disconnection and the warning circuit of the light failure sensor is activated.
As a result, the current flows from TERMINAL 4 of the light failure sensor to TERMINAL 11 to GROUND and turns the rear lights warning light on. By pressing the brake pedal, the current flowing to TERMINAL 8 of the light failure sensor keeps the warning circuit on and holds the warning light on until the ignition SW is turned off.
Code | See Page | Code | See Page | Code | See Page |
H4 | 36 | H7 | 36 | H17 | 38 |
H6 | 36 | H9 | 38 | J7 | 38 |
Code | See Page | Relay Blocks (Relay Block Location) |
1 | 18 | R/B No.1 (Instrument Panel Brace LH) |
Code | See Page | Junction Block and Wire Harness (Connector Location) |
3C | 22 | Instrument Panel Wire and J/B No.3 (Instrument Panel Brace LH) |
IB | 20 | Instrument Panel Wire and Instrument Panel J/B (Lower Finish Panel) |
Code | See Page | Joining Wire Harness and Wire Harness (Connector Location) |
CH1 | 42 | Engine Room Main Wire and Instrument Panel Wire (Left Kick Panel) |
HJ1 | 50 | Instrument Panel Wire and Floor Wire (Right Kick Panel) |
Code | See Page | Ground Points Location |
H1 | 50 | Under the Left Center Pillar |
H2 | 50 | Back Panel Center |
[O] : Explains the system outline.
[P] : Indicates reference pages showing the parts locations in the system circuit on the vehicle.
Example : Code 'H4' (Light Failure Sensor) is on page 36 of the manual.
* The first character of the code indicates the alphabetical code allocated to the wire harness, and the second character indicates the serial number of the parts connected to the wire harness.
T'1--Serial number for the connected parts
-Code for the wire harness
[Q] : Indicates the reference page showing the position on the vehicle of Relay Block Connectors in the system circuit.
Example : Connector '1' is described on page 18 of this manual and is installed on the left side of the instrument panel.
Toyota Camry Electrical Wiring Diagram
[R] : Indicates the reference page showing the position on the vehicle of J/B and Wire Harness in the system circuit.
Example : Connector '3C' connects the Instrument Panel Wire and J/B No.3. It is described on page 22 of this manual, and is installed on the instrument panel left side.
[S] : Indicates the reference page describing the wiring harness and wiring harness connector (the female wiring harness is shown first, followed by the male wiring harness).
Example : Connector 'CH1' connects the Engine Room Main Wire (female) and Instrument Panel Wire (male). It is described on page 42 of this manual, and is installed on the left side kick panel.
[T] : Indicates the reference page showing the position of the ground points on the vehicle.
Example : Ground point 'H2' is described on page 50 of this manual and is installed on the back panel center.
The ground points circuit diagram shows the connections from all major parts to the respective ground points. When troubleshooting a faulty ground point, checking the system circuits which use a common ground may help you identify the problem ground quickly. The relationship between ground points ( , and oy shown below) can also be checked this way.
I GROUND POINT
H23 |
(SG) |
Junction Connector
6 (Shielded)
Headlamp Leveling Motor (LH)
L5 | |
Power Window | (E) |
Master SW |
A22 | |
Cooling Fan | (E) |
Motor No.3 |
6 (Shielded)
2008 Toyota Camry Wiring Diagrams
Throttle (L) Position SW
Injection (EI> Pump Assembly
Brake Fluid Level <E> Warning SW
Power Window (E> Master SW
Throttle (L) Position SW
Injection (EI> Pump Assembly
Headlamp Leveling Motor (RH) (RH E) | W - B |
W - B | |
Pressure SW (-S) |
A23 | |
Turn Signal Lamp | W - B |
(Front LH) |
A11 | |
Windshield | (E) |
Wiper Motor |
I9 | |
Headlamp | (E) |
Leveling SW |
Free Toyota Wiring Diagrams
A6 | W - B | g |
Clearance Lamp | ||
(Front RH) |
A21 | |
Clearance Lamp | W - B |
(Front LH> |
(E1) | |
D2 | |
(E01) | Engine ECU |
(E02) |
W - B | Fog Lamp (E) (Front LH) |
W - B | |
Fog Lamp (E) (Front RH) | |
- |
Brake Fluid Level <E> Warning SW
12 7
A1 | |
W - B | Turn Signal Lamp |
(E) (Front RH) |
Power Window (E> Master SW
Option Connector (Vacuum)
(GND) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
B19 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Skid Control ECU | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
with Actuator | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
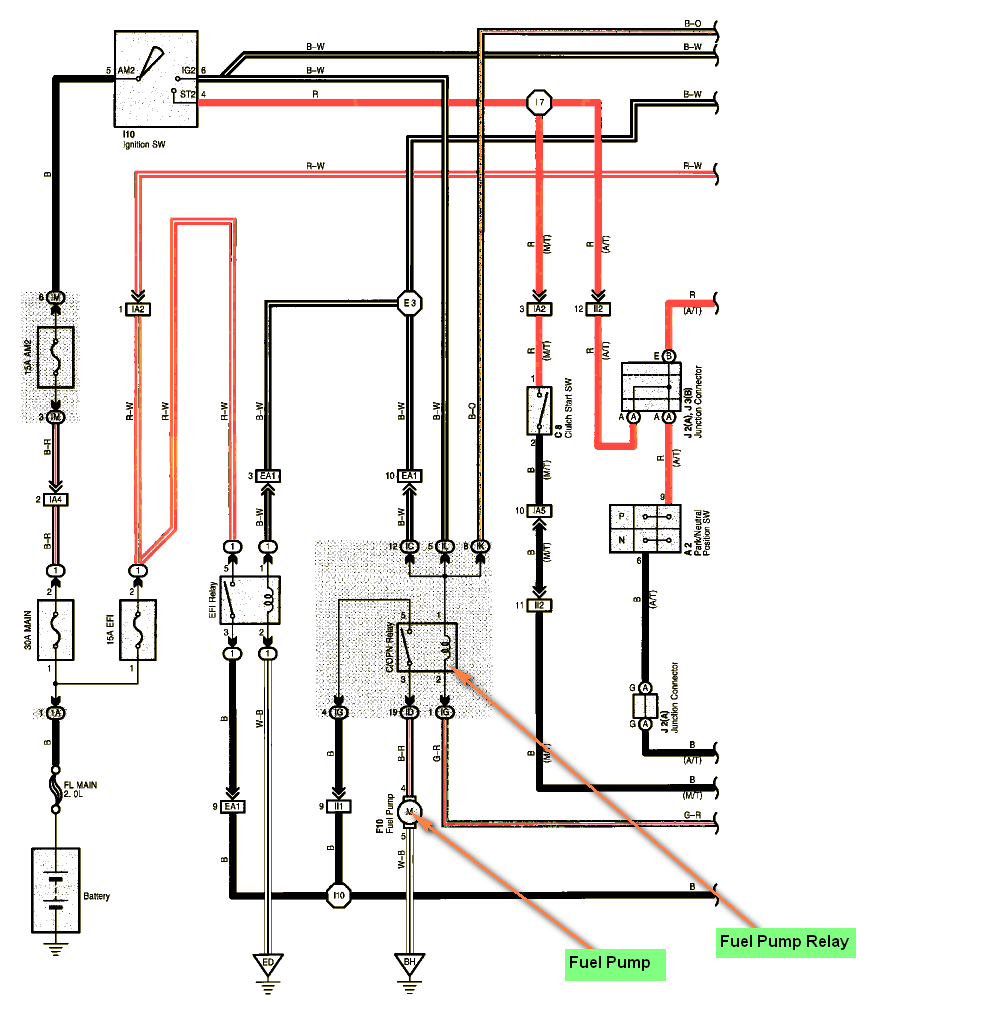
* The system shown here is an EXAMPLE ONLY. It is different to the actual circuit shown in the SYSTEM CIRCUITS SECTION. The 'Current Flow Chart' section, describes which parts each power source (fuses, fusible links, and circuit breakers) transmits current to. In the Power Source circuit diagram, the conditions when battery power is supplied to each system are explained. Since all System Circuit diagrams start from the power source, the power source system must be fully understood. J POWER SOURCE (Current Flow Chart)_ The chart below shows the route by which current flows from the battery to each electrical source (Fusible Link, Circuit Breaker, Fues, etc.) and other parts Fusible Link Block
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||